Flexibilidade Versátil de Design e Capacidades de Integração
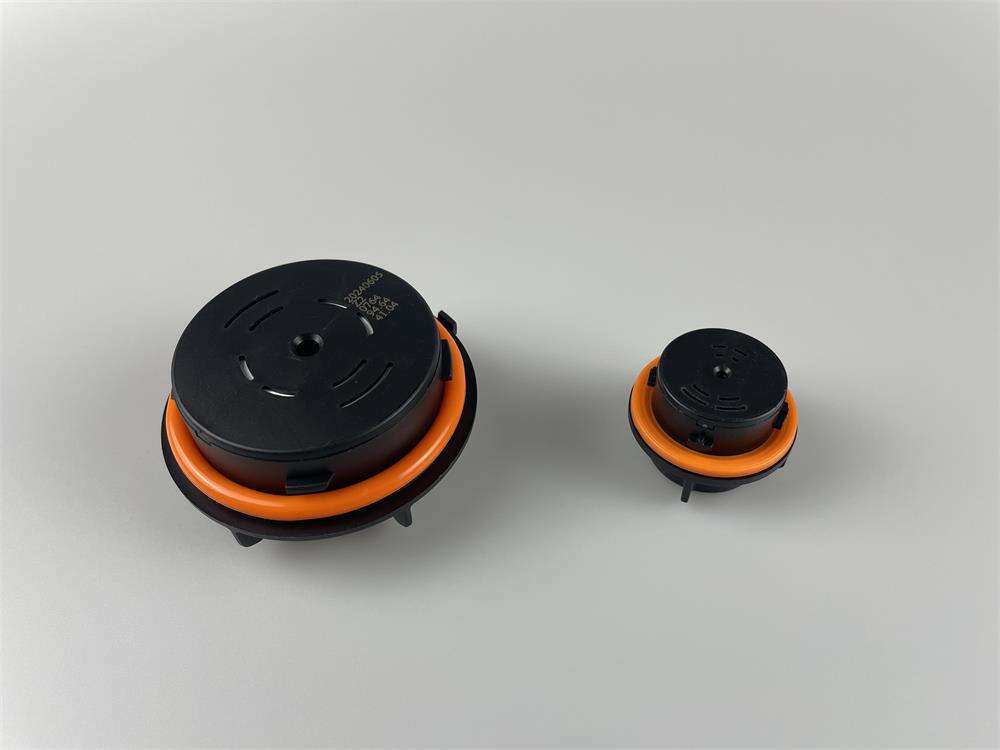
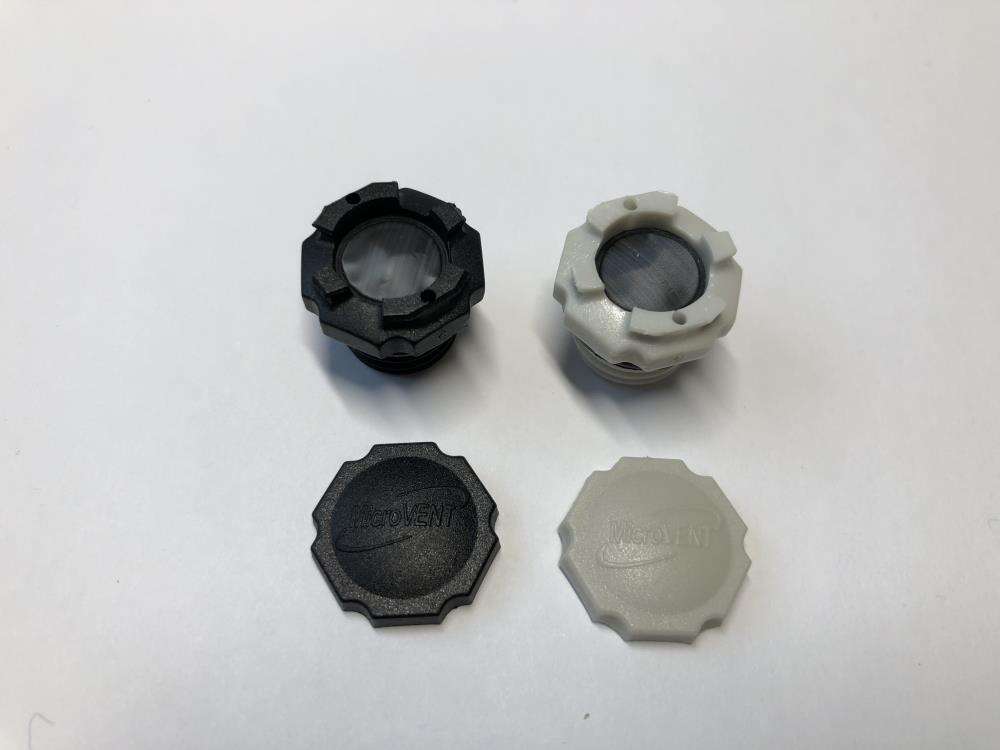
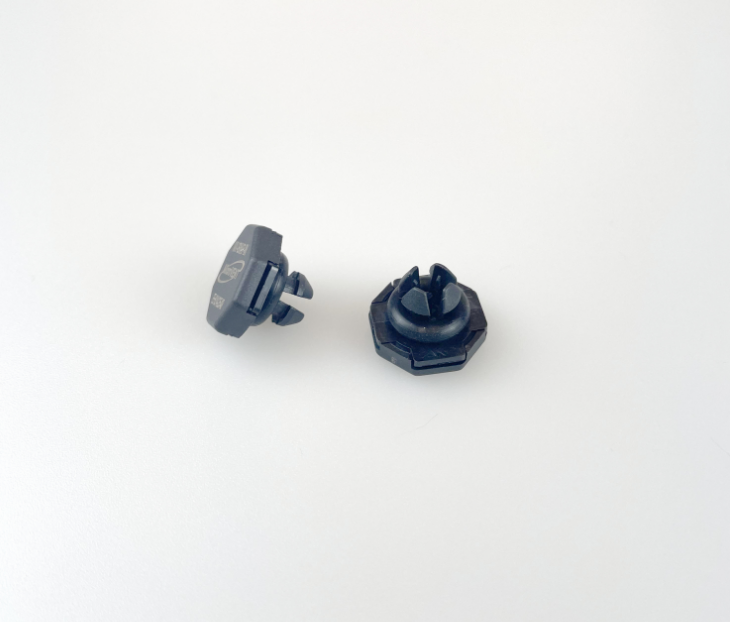
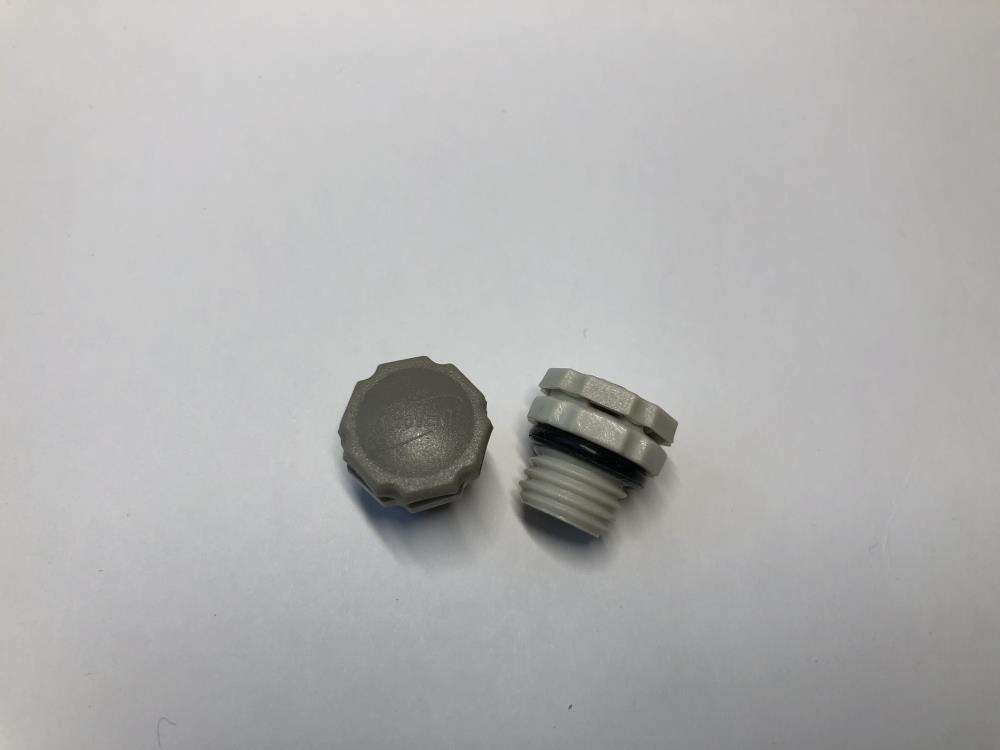
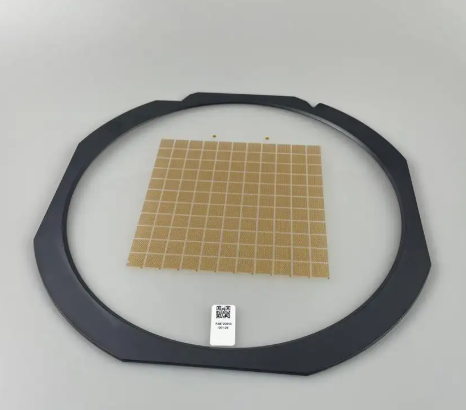
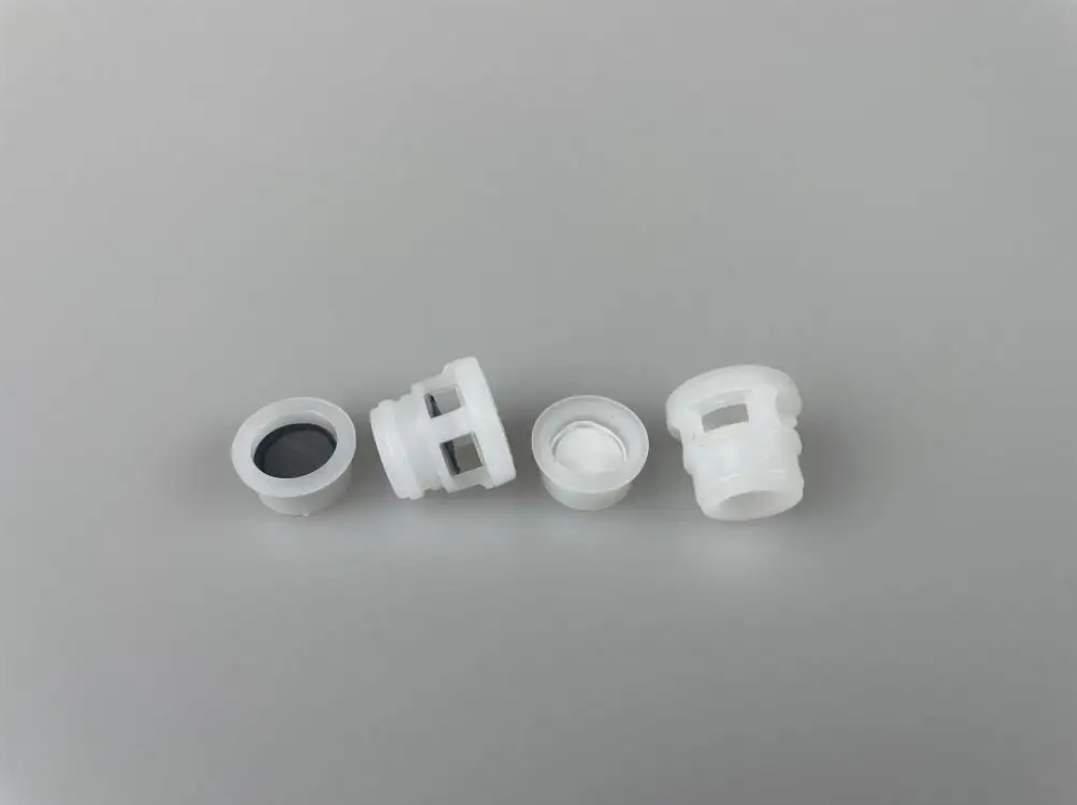
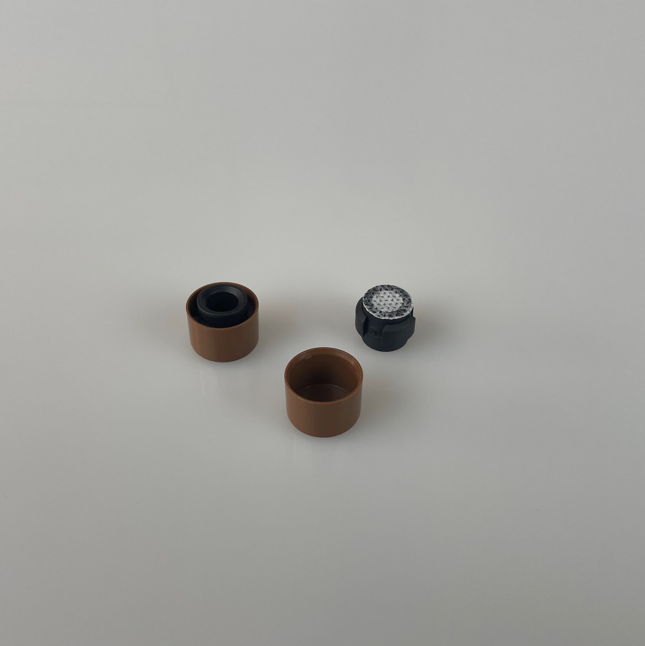
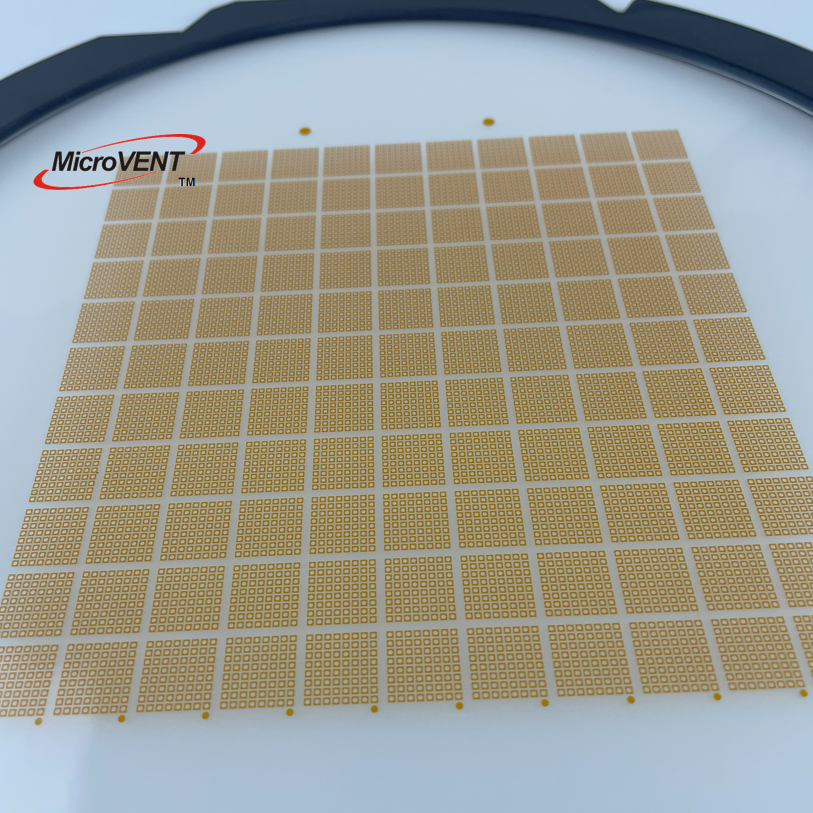
A notável flexibilidade de design do ePTFE MEMS permite a integração perfeita em diversas aplicações, oferecendo soluções personalizadas para requisitos específicos de desempenho. Essa adaptabilidade decorre das capacidades únicas de processamento do material, que permitem sua fabricação em várias configurações, incluindo membranas planas, estruturas pleats, formas tubulares e geometrias tridimensionais complexas. O material pode ser laminado com substratos de apoio, como tecidos não tecidos, tecidos planos ou chapas metálicas perfuradas, para aumentar a resistência mecânica, preservando ao mesmo tempo suas propriedades de barreira. Essas estruturas compostas combinam a excelente filtragem do ePTFE MEMS com o suporte estrutural necessário para aplicações exigentes. A conformabilidade do material permite que ele siga contornos superficiais complexos e formas irregulares, assegurando vedação e proteção eficazes em ambientes de instalação desafiadores. Técnicas de modificação superficial podem ser aplicadas ao ePTFE MEMS para realçar propriedades específicas, como hidrofilicidade, adesão ou atividade antimicrobiana, ampliando ainda mais seu leque de aplicações. Essas modificações podem ser obtidas por meio de tratamento com plasma, enxertia química ou aplicação de revestimentos, sem comprometer as características de desempenho do material base. O processo de fabricação permite um controle preciso da espessura, normalmente variando de 10 mícrons a vários milímetros, possibilitando a otimização conforme os requisitos específicos da aplicação. Membranas mais finas proporcionam maior permeabilidade para aplicações que exigem vazões máximas, enquanto variantes mais espessas oferecem maior resistência mecânica para aplicações de alta pressão. A soldabilidade e capacidade de união do material facilitam a integração com diversos materiais de carcaça e componentes do sistema, utilizando técnicas padrão de junção, como soldagem térmica, colagem por ultrassom ou fixação com adesivo. Padrões personalizados de perfuração podem ser incorporados para criar soluções de ventilação com características de fluxo específicas ou para fornecer reforço em áreas de alto estresse. A escalabilidade da produção de ePTFE MEMS permite a fabricação econômica tanto para quantidades de protótipos quanto para aplicações de grande volume, tornando-o acessível a diversos segmentos de mercado. Medidas de controle de qualidade garantem propriedades consistentes entre lotes de produção, fornecendo aos engenheiros parâmetros de projeto confiáveis para a otimização do sistema.
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 CS
CS
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 ID
ID
 VI
VI
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 MS
MS